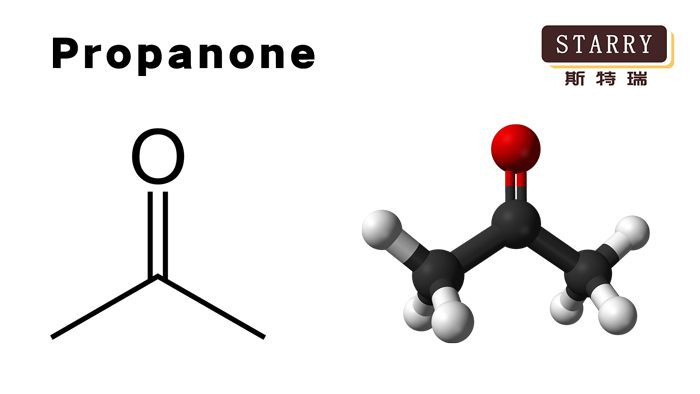
Propanone, also known as Acetone, is a colorless and volatile liquid that has a wide range of properties and uses, and CAS Number: 67-64-1, UN Number: 1090. In this blog post, we will explore some of the key characteristics and applications of propanone.
One of the notable properties of propanone is its ability to easily dissolve in water and other organic solvents. This makes it an excellent solvent for various substances, including paints, varnishes, and adhesives. Its ability to dissolve both polar and nonpolar compounds makes it a versatile choice in many industries.
Propanone is highly volatile, meaning it evaporates quickly at room temperature. This quality makes it an ideal solvent for removing grease, oil, and other contaminants from surfaces. Many industries, such as automotive and electronics, rely on propanone as a cleaning agent for their production processes.
Another notable application of propanone is in the production of plastics and synthetic fibers. It is a key ingredient in the manufacturing of polystyrene, acrylic, and polyester, among others. Its ability to dissolve various polymers and resins makes it an essential component in these processes.
Propanone also finds use in the pharmaceutical industry as a solvent for medications and in the production of pharmaceutical intermediates. Its role in drug formulation and synthesis is crucial in ensuring the effectiveness and stability of pharmaceutical products.
In addition to its industrial applications, propanone is commonly used as a nail polish remover and as a solvent in personal care products such as cosmetics and perfumes.
In conclusion, propanone is a versatile and widely used chemical compound. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances, its volatility, and its role in plastics manufacturing and pharmaceuticals make it an essential component in various industries.



